ITR Filing in India: Your Complete Guide

ITR Filing in India: Your Complete Guide
In India, Income Tax Return (ITR) filings are essential. They capture your financial activity during a fiscal year—income, investments, deductions, and taxes paid. ITR reflects your contribution to public services and infrastructure. Whether individual, business, or professional, understanding ITR’s significance ensures tax compliance and supports national progress. This article simplifies ITR filings in India, highlighting their importance and procedural aspects.
IndiaFilings can simplify the ITR filing process for a stress-free experience. We are here to guide you through your income tax requirements.
File ITR Now!Income Tax: What It Means
Income tax is like a part of your earnings that you give to the government. The government uses this money to ensure people have good healthcare, good schools, help farmers, and improve roads and buildings. Everyone who earns money, whether individuals, families, or companies, must give some of it as income tax. The amount you give depends on how much you earn. The government decides how much you need to give based on the rules they make.
Income Tax Return (ITR)
An Income Tax Return (ITR) is a document through which taxpayers provide details about their earned income and the corresponding tax obligations to the income tax department.
The tax department has introduced seven distinct forms: ITR 1, ITR 2, ITR 3, ITR 4, ITR 5, ITR 6, and ITR 7. Every taxpayer must complete and submit their ITR within the specified deadline. The choice of ITR form depends on factors such as the taxpayer’s income sources, earned income amount, and taxpayer category (individuals, HUFs, companies, etc.).
Determining Who Needs to File an Income Tax Return
Filing an income tax return is a legal obligation that varies based on different scenarios. Here’s a breakdown of who should file an income tax return:
- Salaried Individuals: If your gross income surpasses the exemption level before considering deductions under Sections 80C to 80U, you must file an income tax return.
- Firms: Regardless of whether a firm is in profit or loss, entities like private limited companies, LLPs (Limited Liability Partnerships), and partnerships must file their IT returns.
- Directors and Partners: Individuals holding the position of Directors in Private Limited Companies or Partners in Limited Liability Partnership firms are obligated to file an income tax return.
- Dividend Earners: Individuals earning dividends from various sources such as mutual funds, bonds, equities, fixed deposits, and interest, among others, are required to file an income tax return.
- Charity and Religious Trusts: Individuals receiving income from charity or religious trusts and from voluntary contributions are also subject to filing an income tax return.
- Tax Refunds: Individuals and businesses eligible for tax refunds should file an income tax return to claim their rightful returns.
- NRIs and Tech Professionals: Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) and technology professionals also fall under the category of individuals who should file an income tax return based on their income and circumstances.
Mandatory Income Tax Return Filing in India
In India, filing an Income Tax Return (ITR) is obligatory under certain circumstances. If your gross total income exceeds the basic exemption limit, which varies based on age groups, as follows:
- Individuals below 60 years: Rs 2.5 lakh
- Individuals above 60 years but below 80 years: Rs 3.0 lakh
- Individuals above 80 years: Rs 5.0 lakh
Even if your income falls below the basic exemption limit, you are required to file an ITR if you meet any of the following conditions:
- Deposited over Rs 1 crore in a current bank account: Mandatory if you deposited Rs. 1 crore or more in one or more current bank accounts (excluding post office current accounts).
- Deposited over Rs 50 lakh in savings bank account: Mandatory if you deposited Rs: 50 lakh or more in one or more savings bank accounts.
- Spent over Rs 2 lakh on foreign travel: Mandatory if your expenditure on foreign travel exceeds Rs. 2 lahks.
- Electricity expenses exceeded Rs 1 lakh: Mandatory if your electricity consumption expenses during the previous year exceeded Rs. 1 lakh.
- TDS or TCS over Rs 25,000 (Rs 50,000 for senior citizens): Mandatory if your tax deducted at source (TDS) or tax collected at source (TCS) is over Rs. 25,000 (Rs. 50,000 for senior citizens) in the previous year.
- Business turnover over Rs 60 lakh: Mandatory for businesses with total sales, turnover, or gross receipts exceeding Rs. 60 lahks during the previous year.
- Professional income over Rs 10 lakh: Mandatory for professionals with gross receipts exceeding Rs. 10 lahks during the previous year.
Choosing the Right ITR Form: A Quick Guide
Here’s a simplified breakdown of the applicable ITR forms based on different situations:
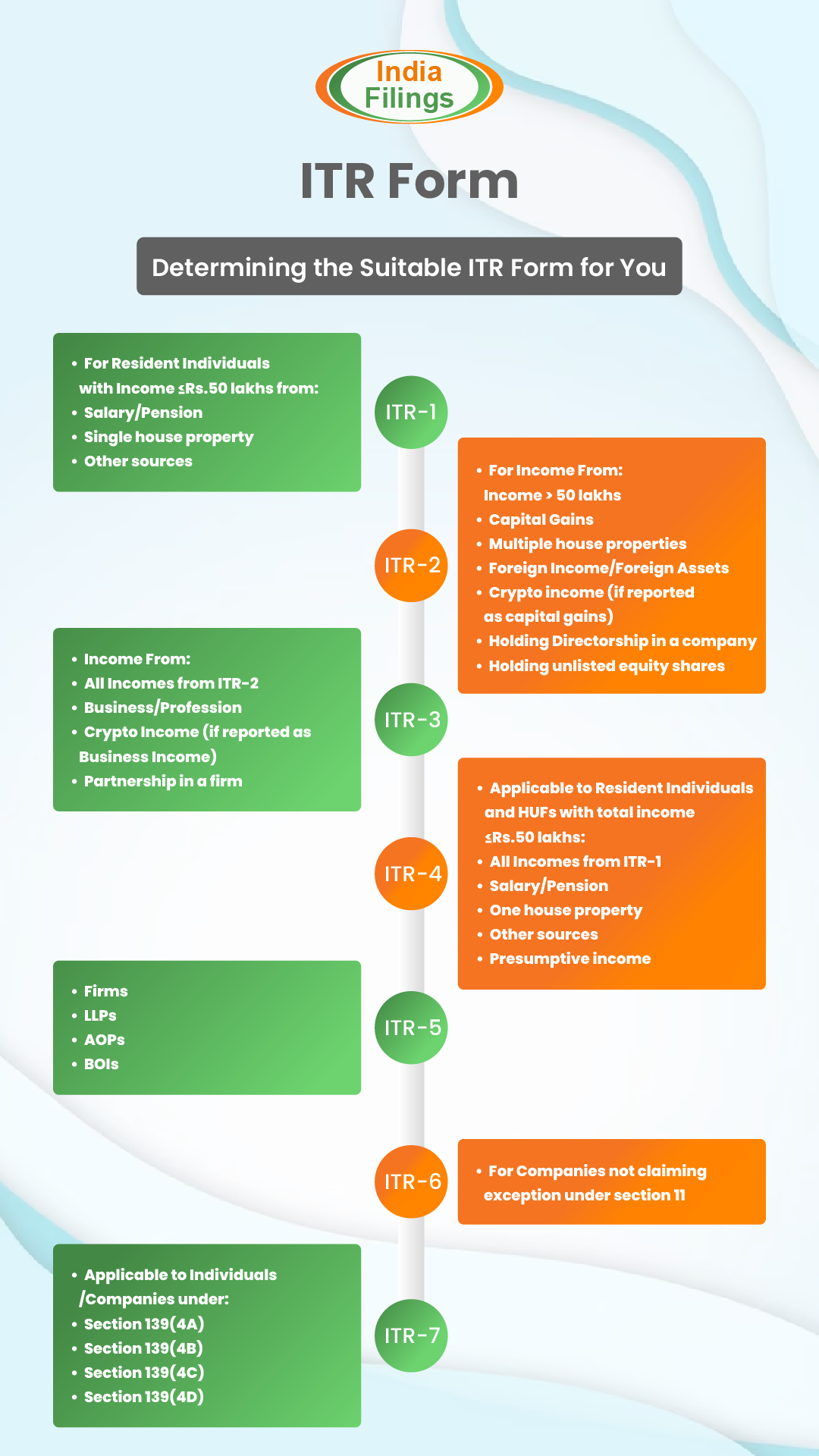
ITR-1: SAHAJ
For individuals with annual income below Rs. 50 Lakhs from salary or pension. Must have only one house property.
ITR-2: Beyond Business
Suitable for NRIs, Directors of Companies, and shareholders of private companies. If you have capital gains income, foreign income, or own two or more house properties. Applicable for income exceeding Rs. 50 lakhs.
ITR-3: Professionals and Proprietorships
For professionals and those running a proprietorship business in India.
ITR-4: Presumptive Taxation Enrollees
Suppose you’re under the presumptive taxation scheme. Business income should be less than Rs. 2 crores, or professional income less than Rs. 50 lakhs.
ITR-5: Partnerships, LLPs, and More
Must be filed by partnership firms, LLPs, associations, and bodies of individuals.
ITR-6: Companies
For companies registered in India.
ITR-7: Special Entities
Applicable to entities like charitable/religious trusts, political parties, scientific research institutions, and colleges/universities.
Benefits of ITR Filing
- Valid Proof of Income: Submitting your ITR is legitimate proof of your income. This documentation can be valuable in various scenarios, from financial transactions to legal matters.
- Facilitates Future Loan Applications: Financial institutions often require ITR as an essential document when seeking loans in the future. A filed ITR demonstrates your financial stability and repayment capacity.
- Essential for Credit Card Applications: Applying for credit cards from banks necessitates the submission of your ITR. This practice helps banks evaluate your creditworthiness and credit limit eligibility.
- Vital for VISA Applications: ITR holds importance in applying for visas, especially for foreign travel. Authorities often use ITR to prove your financial standing and ties to your home country.
E-Filing of Income Tax Return (ITR)
“E-Filing of Income Tax Return (ITR)” refers to electronically submitting your income tax return to the tax authorities using online platforms and digital means. Instead of submitting a physical paper document, individuals and entities can file their tax returns electronically through official websites or designated online portals provided by the tax department. This electronic filing system simplifies and accelerates the process of submission of tax returns, making it more convenient, efficient, and environmentally friendly than traditional paper-based methods.
Essential Documents for Income Tax Return (ITR) Filings
Before delving into the steps involved in e-filing ITR, taxpayers must gather specific documents, including:
- Permanent Account Number (PAN)
- Form 26AS and other relevant statements
- Bank statements
- Form 16
Step-by-Step Guide to E-File ITR on the Income Tax Portal
Step 1: Log in to the Portal
Go to the official Income Tax e-filing website and click the ‘Login’ option. Enter your PAN in the designated User ID field. Click on ‘Continue’. Verify the security message by checking the tickbox. Enter your password and Click on ‘Continue.’
Step 2: Access ‘File Income Tax Return’
Click on the ‘e-File’ tab and Choose ‘Income Tax Returns.’ Select ‘File Income Tax Return.’
Step 3: Choose the Correct ‘Assessment Year’
Pick the ‘Assessment Year’ and Select the mode of filing as ‘Online.’
Step 4: Select Filing Status
Pick your filing status from Individual, HUF, or Others. Opt for ‘Individual’ and proceed by clicking ‘Continue.’
Step 5: Choose the Appropriate ITR Type
Determine the correct ITR form based on your circumstances. There are 7 ITR forms available. For instance, if you’re an individual or HUF with capital gains but no income from business or profession, use ITR 2. Ensure you are selecting the correct ITR type.
Step 6: Specify the Reason for Filing ITR
Indicate the reason for filing your returns. Select the suitable option that applies to your situation:
- Taxable income exceeds the basic exemption limit
- Mandatory filing due to specific criteria
- Other reasons
Step 7: Add Bank Account Details and Review Information
Input your bank account details, ensuring they are accurate and pre-validated if previously provided.
- Proceed to the next page with pre-filled details.
- Thoroughly review the information for correctness.
- Confirm the summary of your returns and validate the provided details.
Step 8: E-Verify Your ITR
The final and crucial step is to verify your return. Failure to verify is equivalent to not filing at all.
Choose from verification methods like Aadhaar OTP, electronic verification code (EVC), Net Banking, or sending a physical copy of ITR-V to CPC, Bengaluru.
Filing Income Tax Return for Previous Years
To file your income tax return for previous years, you can utilize the ITR U form. However, there are specific conditions and limitations regarding eligibility and the duration during which ITR-U can be employed.
Understanding Belated Return
A Belated Return refers to filing your income tax return after the original due date has passed. For instance, you can file a Belated Return if you can’t submit your ITR by the initial deadline of 31st July for the financial year 2022-23. This allows you to submit your return after the original due date but before the extended deadline, typically until 31st December.
Late Filing Fees under Section 234F:
Starting from the fiscal year 2017-18, a late filing fee is applicable if you submit your income tax returns after the due date, as outlined in Section 234F.
For instance, consider the due date for filing returns for the fiscal year 2021-22, set at 31st July 2022. If you miss this deadline and opt for a belated return, you can file until 31st December 2022.
However, it’s important to note that a late filing penalty will be imposed. If you file your ITR after the due date (31st July 2022) but before the extended deadline (31st December 2022), a maximum penalty of Rs 5,000 will be levied.
However, a provision exists to provide relief to small taxpayers. If your total income does not exceed Rs 5 lakh, the maximum penalty for the delay will be capped at Rs 1,000.
Latest Update on the Pay Later Option for Income Tax Filing
The Income Tax e-filing portal has recently rolled out a ‘Pay Later’ option, allowing you to complete your tax filing process before making any tax payments. You can pay taxes after you are done filing. For additional information, please refer to our guide – Pay later option for the Income tax return filing.
Simplify ITR Filing with IndiaFilings: Your Hassle-Free Solution
Navigating the intricacies of income tax return filing can be a daunting endeavor. However, with IndiaFilings by your side, this process becomes remarkably streamlined, requiring three simple steps. Our dedicated team of experts is available round-the-clock to ensure your income tax returns are filed online efficiently and promptly. Why tackle the task independently when our seasoned professionals can swiftly handle it for you? Choose IndiaFilings for a seamless ITR filing experience that ensures accuracy and peace of mind.
File ITR Now!

